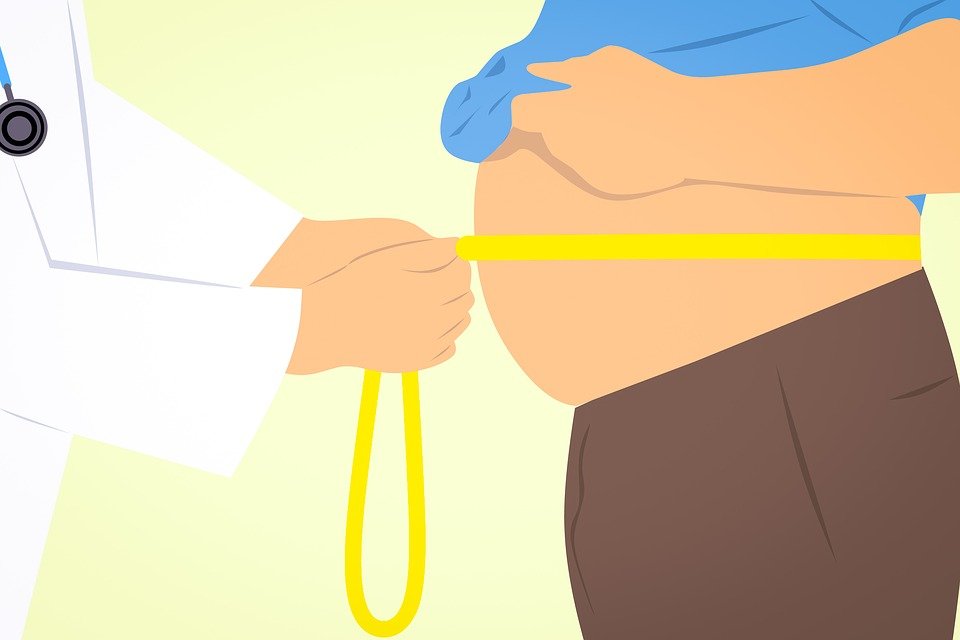
Overweight and obesity are defined as abnormal or excessive fat accumulation that presents a risk to health. A crude population measure of obesity is the body mass index (BMI), a person’s weight (in kilograms) divided by the square of his or her height (in meters). A person with a BMI of 30 or more is generally considered obese. A person with a BMI equal to or more than 25 is considered overweight.
Overweight and obesity are major risk factors for a number of chronic diseases. Here are 20 diseases or conditions that can be attributed to obesity.
- Diabetics
- Cancers have many different forms and types.
- Congestive heart failure
- The enlarged heart is another heart condition
- Pulmonary embolism
- Polycystic ovarian syndrome
- Gastro-esophageal reflux disease
- Fatty liver disease
- A hernia
- Erectile dysfunction
- Urinary incontinence
- Chronic renal failure
- Lymphedema
- Cellulitis is a spreading infection
- Stroke is caused by a lack of blood supply to your brain.
- Sleep apnea
- Depression
- Osteoarthritis
- Uric acid accumulates in your blood.
- Gallbladder disease.
Obesity is a growing problem in the world. It is responsible for 300,000 deaths every year in the United States.